Author: SemiconShorts
-

Verilog or SystemVerilog ?
Verilog and System Verilog (SV) , both are used as HDLs in modern day designs. But there are some differences that one should know, to be able to make a better decision on how to code effectively. Verilog is an older language, which was introduced in 1984. System Verilog is based on Verilog but has…
-
Verilog Constants
Parameter : While coding a Verilog module, there can be a constant value that needs to be used multiple times within the module. Such constants can be declared using ‘parameter’. Advantage : The biggest advantage of using ‘parameters’ is that, the code is scalable. A change in parameter value can be easily accommodated by the…
-

DFT vs DV
Which one should you go for? DFT refers to Design for Test, while DV refers to Design Verification. Both of these job roles are equally challenging and are crucial steps in the VLSI design flow. Lets read what they are about. Sequence of DFT and DV in Design Development: Once the RTL code is done…
-

Microchip World
From Transistors to Microchip – By Ettore Accenti Book Review by Richa Mittal If a semiconductor expert is asked a question like “What’s inside his iPhone?”, the answer cannot be short and simple. The author has answered this question in simple words without excluding the important details. The journey of semiconductors is given in an…
-
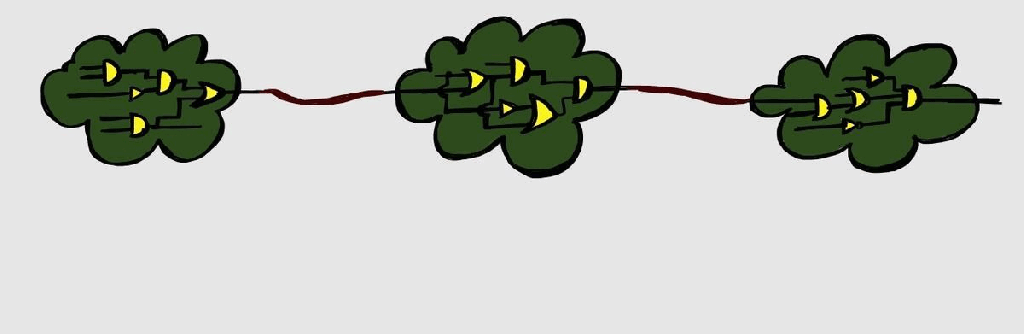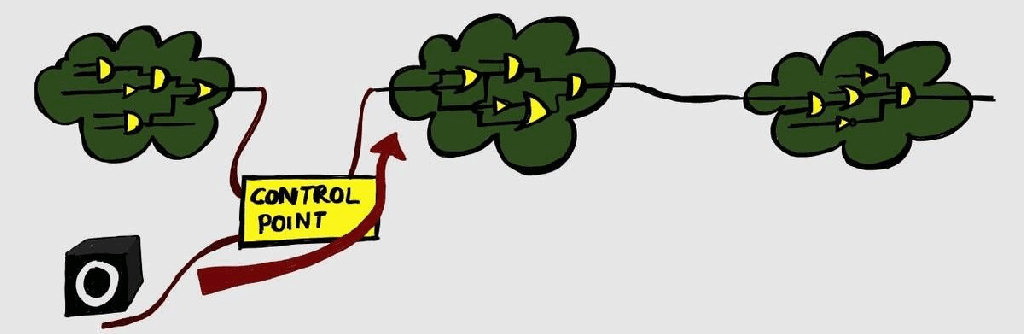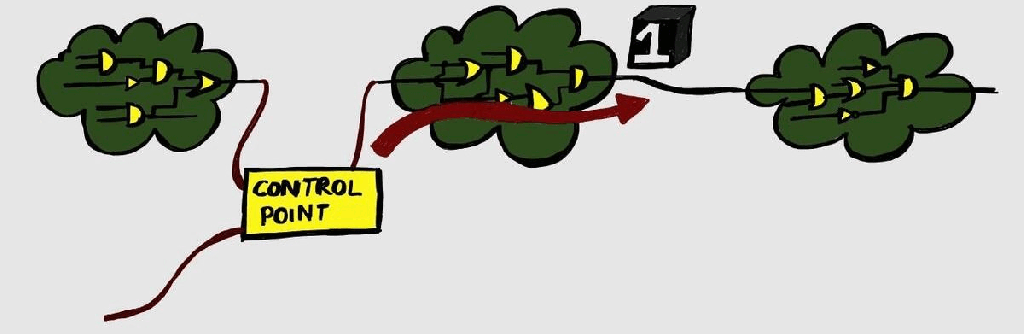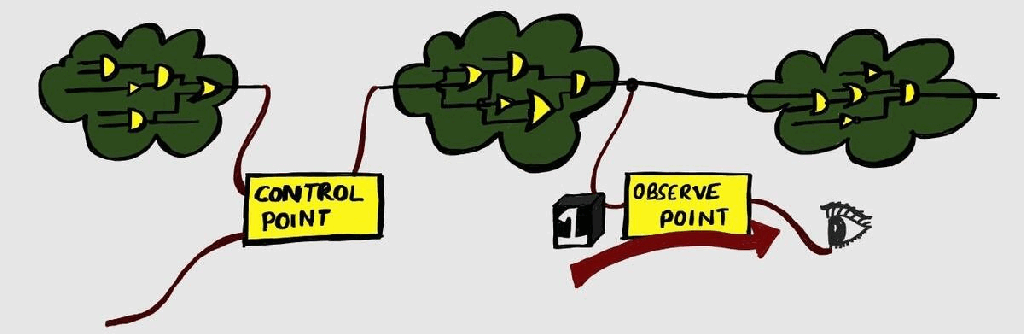
Test-Points
We have discussed DFT and Scan basics in previous articles. Let us talk about another important DFT structure – Test points. The aim of DFT structures is to make the design controllable and observable. We have seen how scan chains allow us to control the design by passing test values, and observing the captured values.…
-
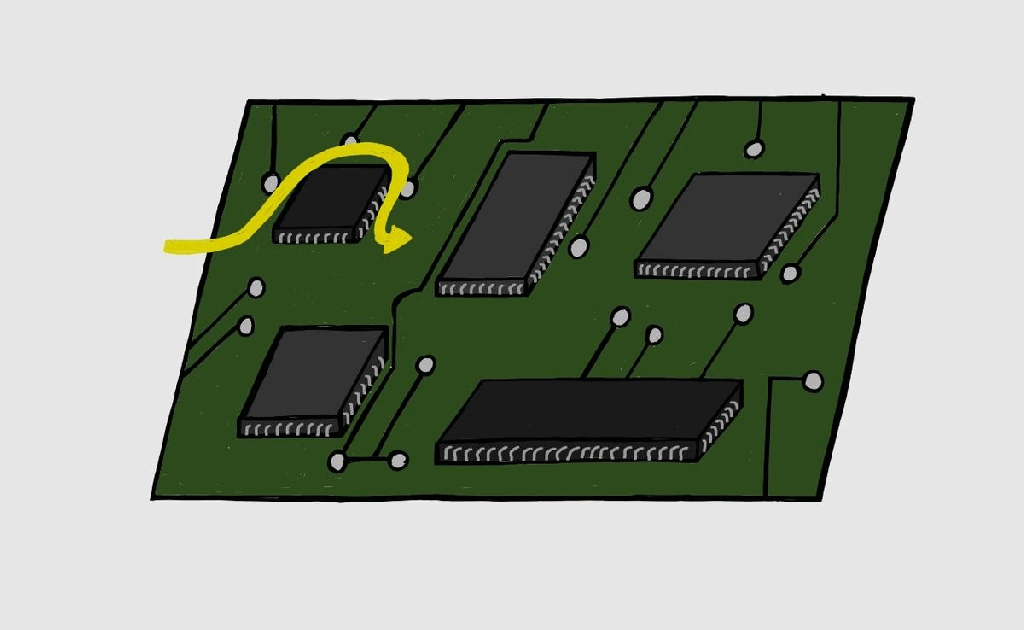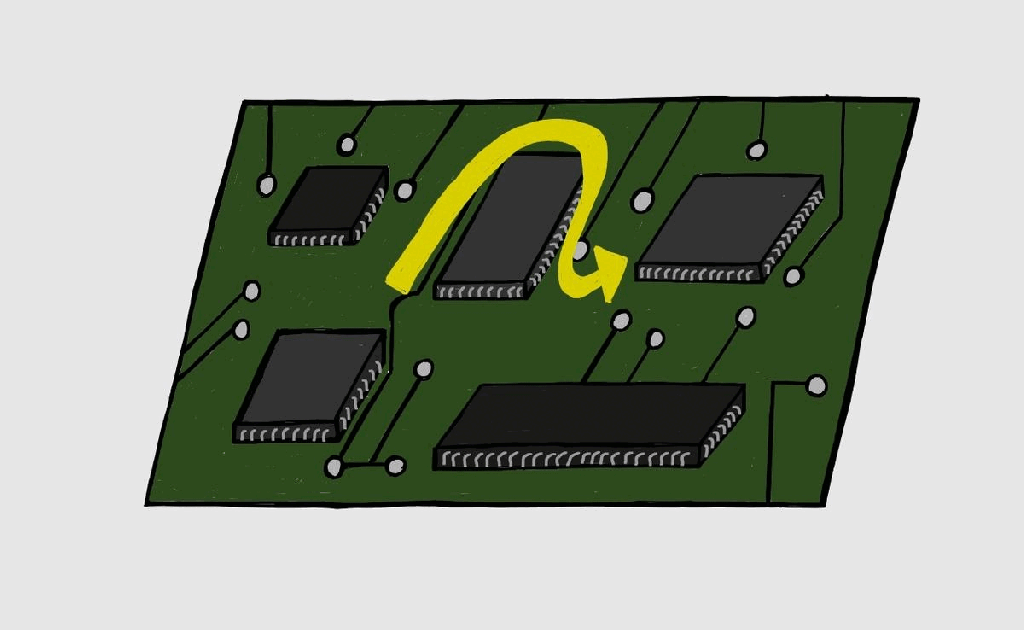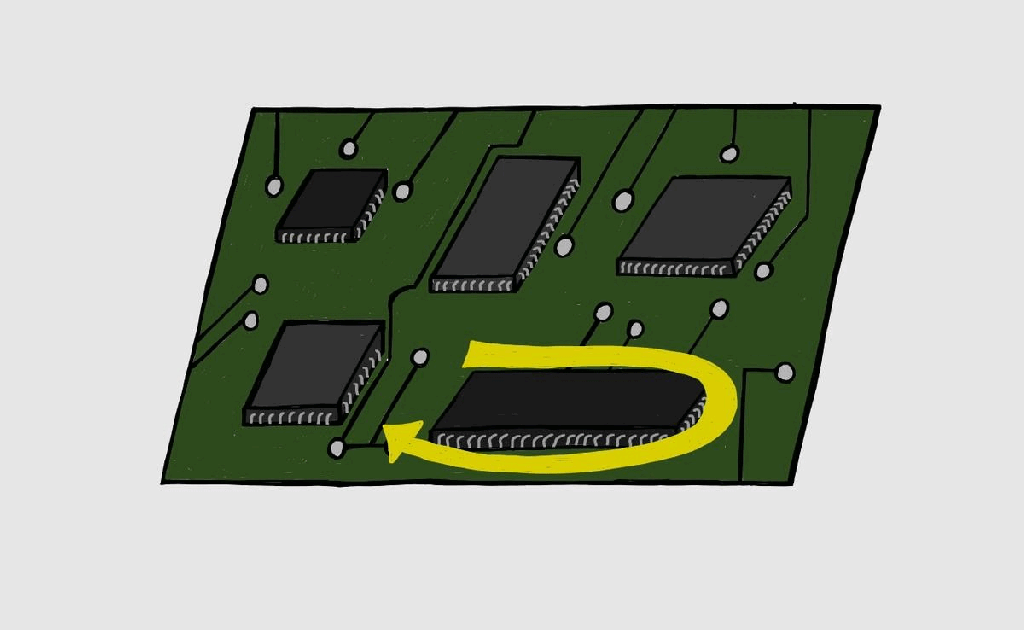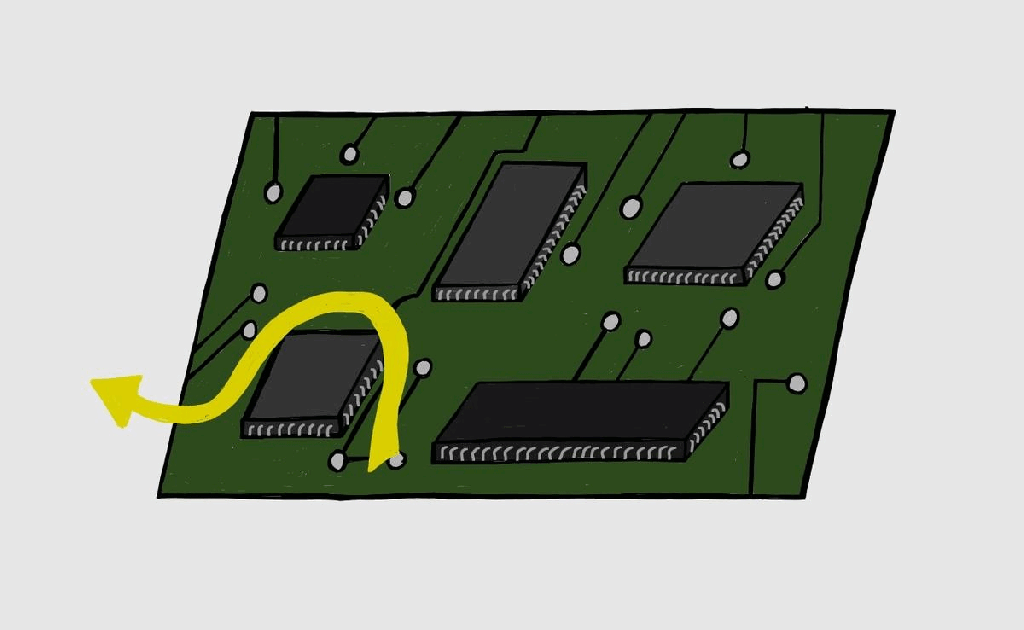
Boundary Scan/JTAG – III
Boundary Scan Registers Boundary scan testing consists of certain registers as mentioned in Boundary Scan-II. There are two kinds of registers: Instruction registers: As the name implies, this register stores the instructions which can be decoded and executed as per requirements. Data registers: Data registers are selected based on the decode instruction from the instruction…
-

Boundary Scan/JTAG – II
As we discussed in “Boundary Scan/JTAG I“, Boundary scan testing is implemented using a JTAG controller. Boundary scan testing was built to test the interconnections between different chips, and JTAG plays a crucial role. Here, we are going to discuss how JTAG works. The components of a JTAG interface/controller are connected within a design as…
-

Boundary Scan/JTAG – I
A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembles a number of Integrated circuits and other electrical components. When such an assembly is created, testing the integration is also necessary. As the density of such boards increased and further miniaturisation happened, it became impossible to access all the nodes with physical probes. Hence, the boundary scan testing technique…
-
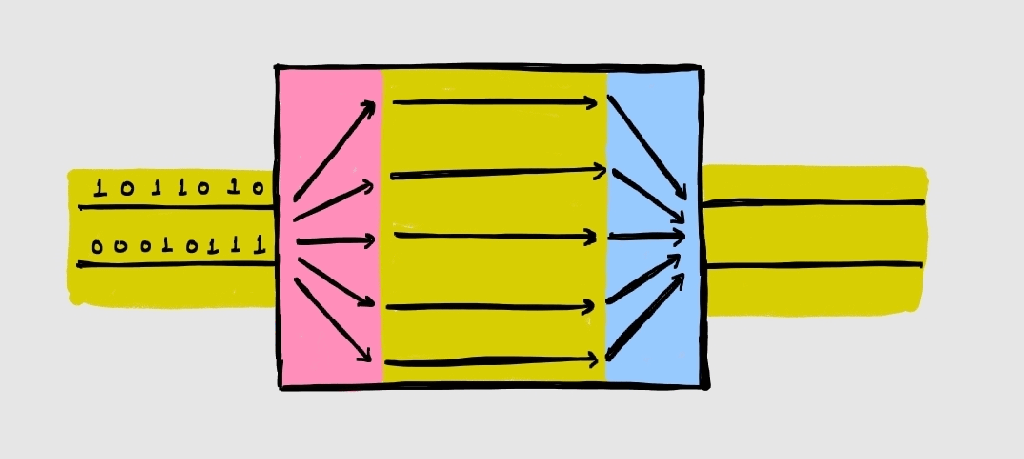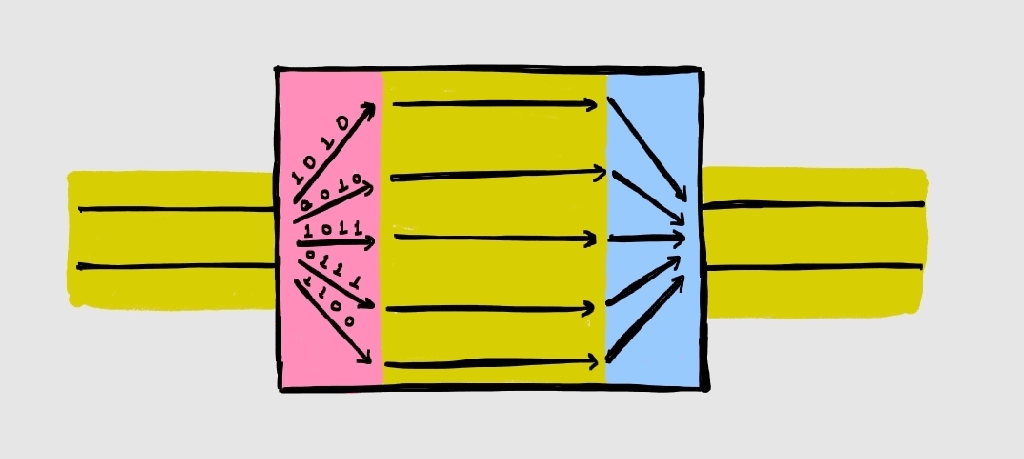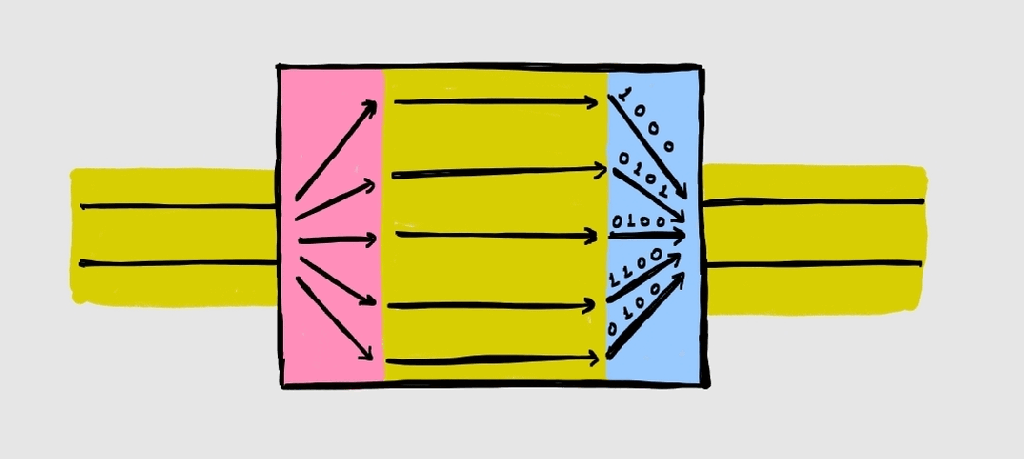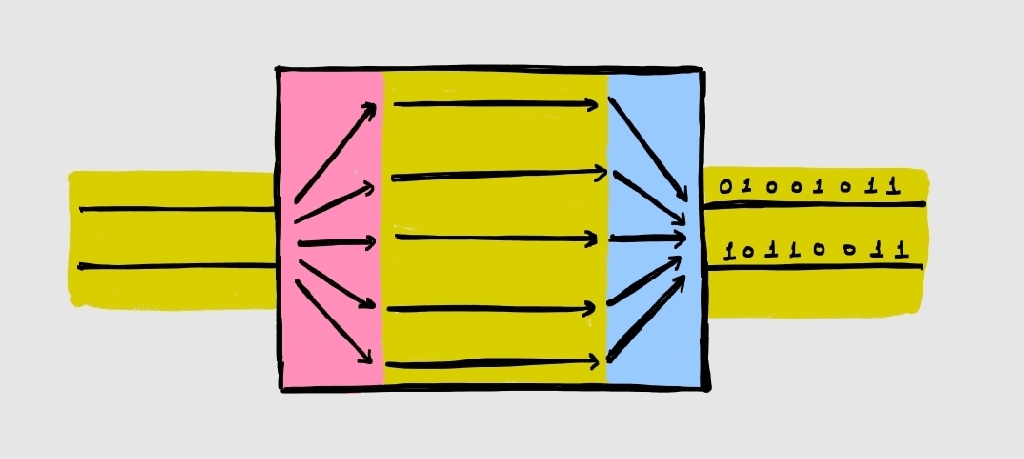
Scan Compression
Understanding scan operation is a pre-requisite to understand scan compression. My article “Scan and Resets” defines scan in simple terms. The basic concept of scan is to convert all flip flops in the design into scannable flipflops (having scan_in, scan_out and scan_enable) and connect them to form scan chains. Theoretically, there is no limit on…
-
Storage Devices – ROM
Rom- Read only Memory is the memory which retains data even after the power is switched off. This non-volatile property of ROMs makes it useful for a lot of applications (as simple as memory which stores boot-up information of your laptop). Let us understand the ROMs structure, as memories are integral part of any chip…