The functioning of any VLSI chip needs some data to boot-up the device. This data can be stored in flash, NVMs which costs more. A good alternative is to use efuse based memories. They allow us to store a small amount of data (which can be programmed only once). Other kinds of information that most chips store in such memories can be:
- Mac addresses
- Device ID
- Calibration Information
- Software specific configurations
They are basically used as One Time Programmable ROMs. The data is stored by programming the efuse. The efuse is ‘blown’ using the principles of Electromigration.
Let us understand the principle of electromigration:
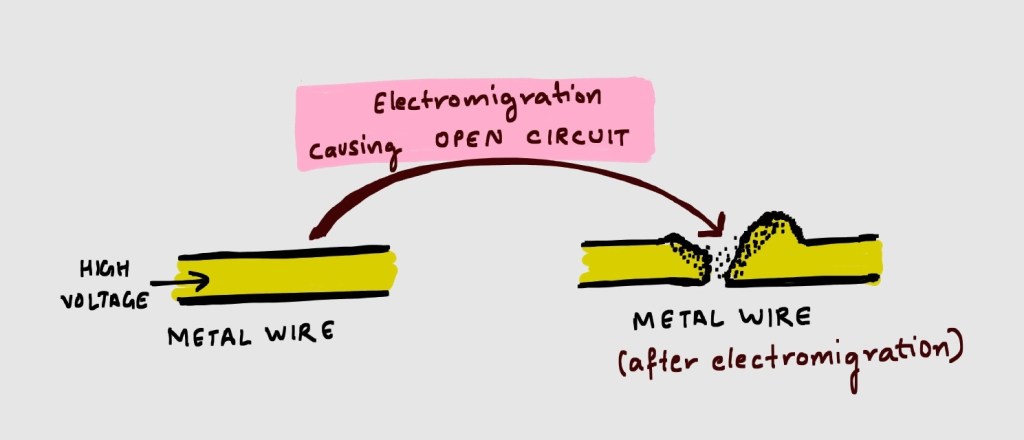
Electromigration is the phenomenon where the conductor material can move. When high voltage or potential is applied across a metal interconnect, it sets up an electric field from positive to negative. This field generates momentum in the electrons which forces them to move in opposite direction (to the field). These electrons collide with the metal ions, which breaks them and metal ions start moving. After sometime, when the current density is high, this movement of ions results in shift or break in the cross sectional area of metal interconnect. This leads to the introduction of very high resistance along the metal interconnect, leading to open circuit.
The metal structure in efuse based memories is silicided polysilicon, which undergoes electromigration when high voltages are applied. The structure is as follows:

Programming:
The process of programming is:
- High voltage is applied at the anode
- Large current flows through fusible link
- nMOS is switched ‘on’ to provide a path from Vdd to Ground (gnd)
- Due to high current, electromigration occurs, and high resistance along fusible link is setup (i.e. fuse is blown)
The time duration for which nMOS is kept ‘ON’ is considered as the ‘programming time’ of the efuse, as this is the duration where high current density blows up the fuse.
Reading:
The values are read as follows:
- ANODE is held at ground
- nMOS is turned OFF
- Sense is performed at Vsense node.

Intact or programmed state is determined accordingly by the ‘sense’ function and reflected as digital output ‘0’ or ‘1’.
Some disadvantages of such memories are:
- Low scaling capacity to lower technology nodes
- Smaller capacity
- Not so small area
- Possibility of regrowth (metal lines can unintentionally get connected again causing the loss of data)
Leave a comment